Since its birth in the 1980s, the Internet has always used TCP as the backbone of its HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), the protocol that organizes the transfer of information on the web. However, the network of almost 40 years ago has little to do with the current one. Its worldwide penetration, the number of users and connected devices and the volume of data handled have multiplied. And this, in turn, drives the demand for faster and more secure communications. Hence, the next step forward for the Internet is to leave TCP behind in what will be the third generation of HTTP: HTTP / 3.
What is HTTP / 3 and how does it work?
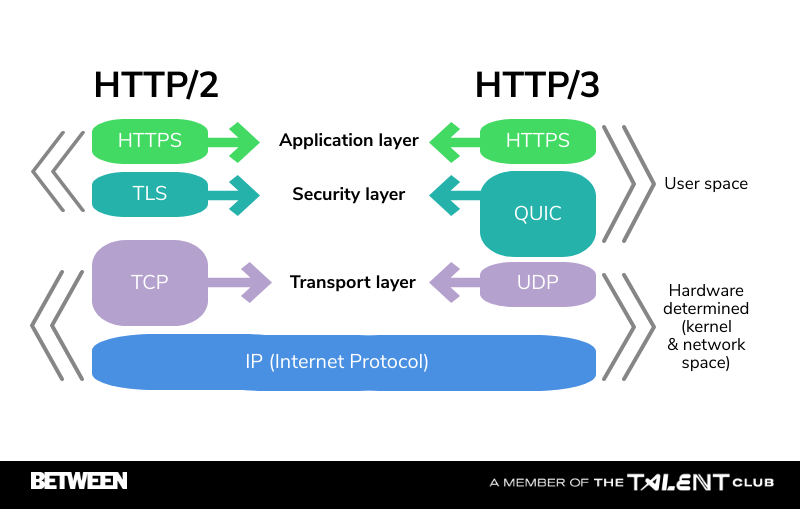
HTTP / 3 is the third adaptation of the HTTP protocol. Unlike the first and second versions of HTTP, which are based on TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), HTTP / 3 uses QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections), a new open source standard initially developed by Google. HTTP / 3 will provide faster and more reliable connections in those contexts where improving latency is essential, for example, in the development of the Internet of Things and in mobile browsing.
The secret of QUIC lies in the fact that it is based on UDP (User Datagram Protocol), an alternative protocol to TCP that differs from the latter because:
- Before proceeding with the data transmission, TCP always verifies the connection between source and destination and, afterwards, the reception of each packet before continuing with the sending.
- UDP, on the other hand, sends the data packets without carrying out checks on the connection or waiting for acknowledgments. If a packet is lost, UDP trusts that the applications themselves are responsible for requesting the missing information again.
This makes UDP, which has previously been used mainly for streaming video and for network gaming, faster than TCP.
QUIC is built on top of UDP but incorporates improvements in the transport layer that deal with security, error detection and resolution, and control of saturation. However, QUIC and HTTP / 3 are still under development by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), which published the latest draft on the progress of the project in February 2020.

How is HTTP / 3 different from HTTP / 2?
HTTP / 3 has key differences from its predecessor, HTTP / 2. We highlight two of them:
- By opting for QUIC, HTTP / 3 overcomes the TCP limitations to which HTTP / 2 is subject, such as the obligation to wait for a response to continue transferring data packets. Furthermore, the connections are 0-RTT (Round-Trip Time), since in HTTP / 3 the information begins to be sent without having to carry out preliminary exchanges to establish communication.
- HTTP / 3 uses TLS 1.3, which increases the level of protection against cyber-attacks by encrypting much of the process and reducing the number of roundtrips required to complete it.
On the other hand, the most notable similarity between HTTP / 2 and HTTP / 3 is that they both use multiplexing, the main novelty introduced by the second generation of the HTTP protocol. Multiplexing allows you to maintain several simultaneous communications through the same channel. Using an analogy, it is as if we had several operators working as a team, instead of a single person doing round trips to move packages one by one.
Who already uses HTTP / 3?
According to W3Techs, in April 2020 5.5% of websites were already using HTTP / 3. This percentage may seem quite low, but it takes on a new meaning if we consider that the list includes names such as Google, YouTube, Facebook or WhatsApp. Do you wonder if the website you are browsing has incorporated HTTP / 3? Well, do not stay with the desire to know. There are tools that allow you to discover it in a few seconds, such as LiteSpeed's HTTP / 3 Check.
HTTP / 3 is still a long way from becoming a standard within transfer protocols, but one thing is clear: it will be another milestone in the history of the Internet. A milestone in which many male and female engineers will leave their mark, like so many open source projects that are enriched every day on the web, either to create machine learning algorithms or to prevent the consequences of the 2038 effect. do you want to participate in the technological advance of the next few years? Review the selection processes open in BETWEEN and dare to level up in your professional career!


